However, this scenario is extremely rare because every transaction always has a corresponding entry on each side of the equation. This simple formula can also be expressed in three other ways, which we’ll cover next. At first glance, this may look overwhelming — but don’t worry because all three reveal the same information; it just depends on what kind of information you’re looking for. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
What is equity?
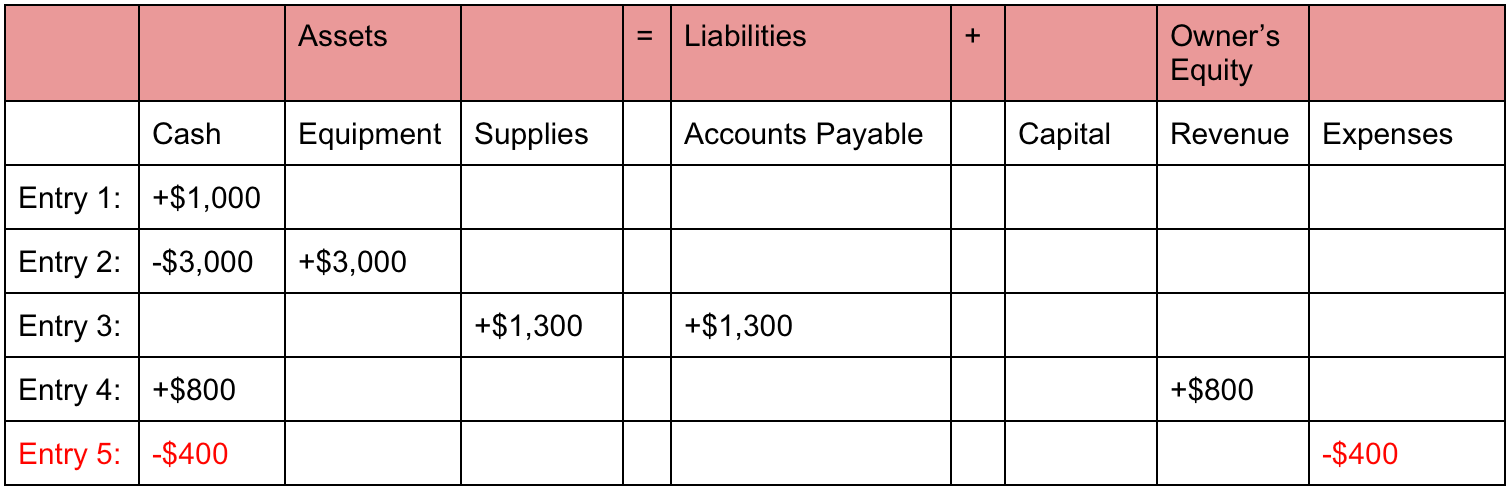
For example, when a company borrows money from a bank, the company’s assets will increase and its liabilities will increase by the same amount. When a company purchases inventory for cash, one asset will increase and one asset will decrease. Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction, the accounting system is referred to as the double-entry accounting or bookkeeping system.
Arrangement #2: Net Value = Assets – Liabilities
- Debt is a liability, whether it is a long-term loan or a bill that is due to be paid.
- The revenue a company shareholder can claim after debts have been paid is Shareholder Equity.
- The combined balance of liabilities and capital is also at $50,000.
- The accounting equation plays a significant role as the foundation of the double-entry bookkeeping system.
- Obligations owed to other companies and people are considered liabilities and can be categorized as current and long-term liabilities.
- Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations.
This basic accounting equation is akin to / identical to the Balance Sheet (aka Statement of Financial Position). They include items such as land, buildings, equipment, and accounts receivable. It is the key to ensuring that each transaction which reflects a debit will always have its corresponding entry on the credit side.
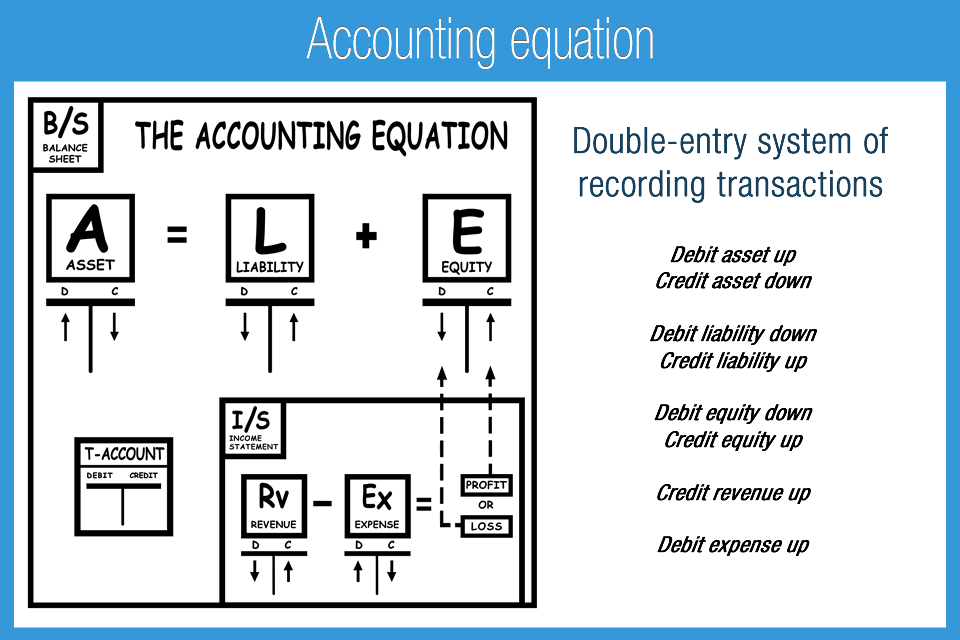
Why must Accounting Equation always Balance?
These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can be recorded in a similar way. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends. Traditionally, this fact is represented in the “double entry bookkeeping” system starting with journal entries. Perhaps the most important part of a “Balance Sheet” (one of five financial statements), ‘Equity’ reflects a firm’s “net worth”, i.e. how much the firm is worth.
Balance Sheet and Income Statement
The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business. In accounting, the claims of creditors are referred to as liabilities and the claims of owner are referred to as owner’s equity. These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bond issues, why choose a career in accounting warranties, and accrued expenses. In this form of the accounting equation, the left hand side (Assets) represents a company’s “resources”. The right hand side of the equation (Liabilities + Equity) shows that company’s “sources of finance”. Equity refers to the owner’s interest in the business or their claims on assets after all liabilities are subtracted.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Where “future economic outflows” is a sophisticated way of saying you expect to pay money. Liabilities on the other hand, are things that we owe, and expect to pay money for. Analyze a company’s financial records as an analyst on a technology team in this free job simulation. Both these arrangements mean the same thing – one just has fewer steps and may be easier to digest for those who aren’t yet familiar with the formula. Still, let’s dive into the differences between the two so that you can understand how each might affect your bookkeeping process.
These are the resources that the company has to use in the future like cash, accounts receivable, equipment, and land. The accounting equation states that total assets is equal to total liabilities plus capital. This lesson presented the basic accounting equation and how it stays equal. The accounting equation equates a company’s assets to its liabilities and equity.
This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments. For a company keeping accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of its accounts. For instance, if a business takes a loan from a bank, the borrowed money will be reflected in its balance sheet as both an increase in the company’s assets and an increase in its loan liability. The accounting equation relies on a double-entry accounting system. In this system, every transaction affects at least two accounts. For example, if a company buys a $1,000 piece of equipment on credit, that $1,000 is an increase in liabilities (the company must pay it back) but also an increase in assets.
Transaction #3 results in an increase in one asset (Service Equipment) and a decrease in another asset (Cash). After the company formation, Speakers, Inc. needs to buy some equipment for installing speakers, so it purchases $20,000 of installation equipment from a manufacturer for cash. In this case, Speakers, Inc. uses its cash to buy another asset, so the asset account is decreased from the disbursement of cash and increased by the addition of installation equipment. Let’s take a look at the formation of a company to illustrate how the accounting equation works in a business situation. To make the Accounting Equation topic even easier to understand, we created a collection of premium materials called AccountingCoach PRO. Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more.
At the same time, it incurred in an obligation to pay the bank. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. When the total assets of a business increase, then its total liabilities or owner’s equity also increase. The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts. Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations.
