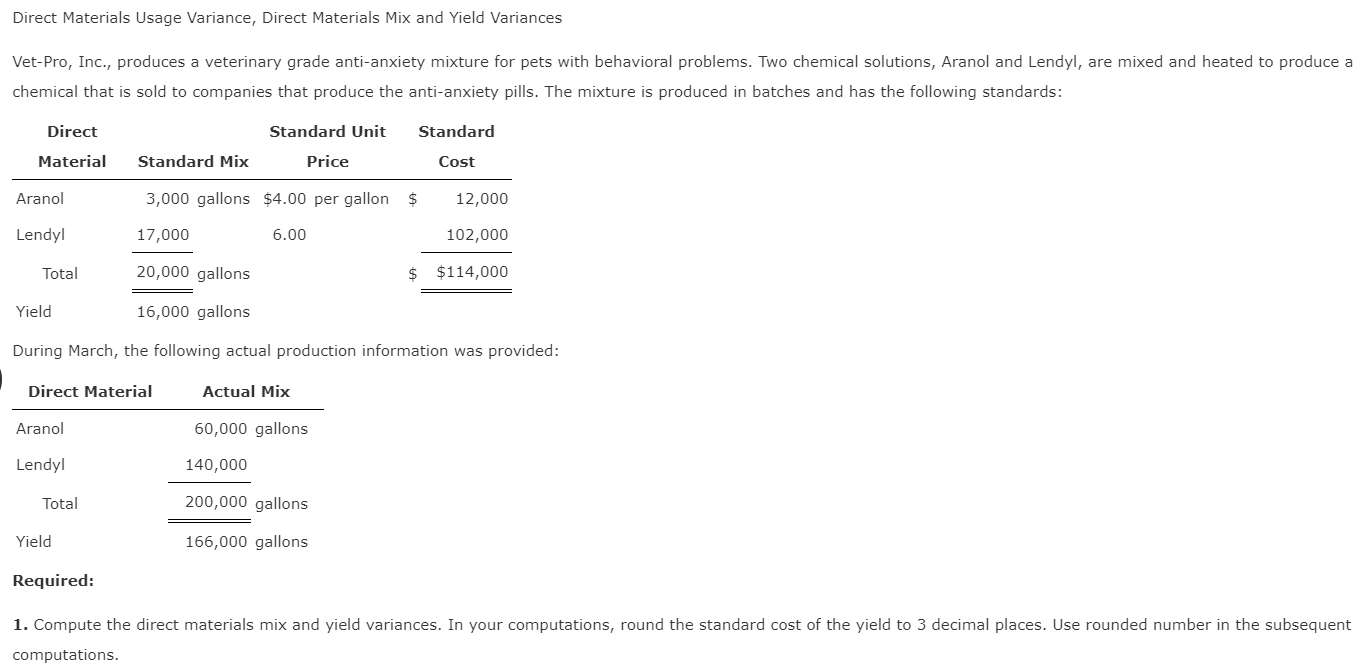
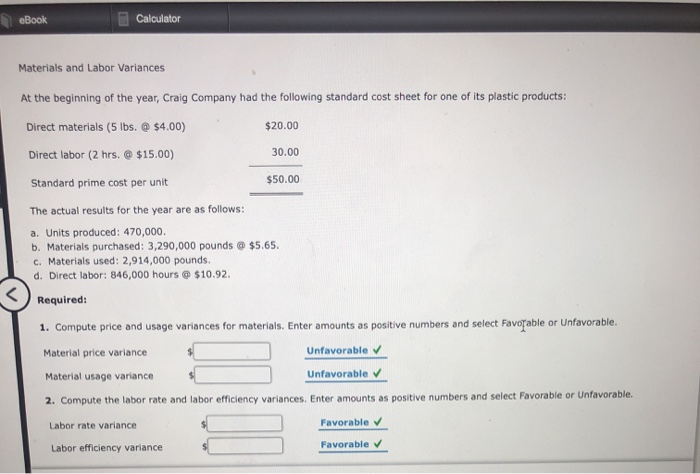
In such situations, a better idea may be to dispense with direct labor efficiency variance – at least for the sake of workers’ motivation at factory floor. Labor variances refer to the differences between the actual labor costs incurred and the standard or expected labor costs for a given production or service period. These variances provide insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of a company’s labor utilization, which is a crucial aspect of cost management and performance evaluation. As with direct materials variances, all positive variances areunfavorable, and all negative variances are favorable.
Variance Analysis
Favorable variances result when actual costs are less than standard costs, and vice versa. The following illustration is intended to demonstrate the very basic relationship between actual cost and standard cost. SQ and SP refer to the “standard” quantity and price that was anticipated. Calculate the labor rate variance, labor time variance, and total labor variance. The direct labor variance measures how efficiently the company uses labor as well as how effective it is at pricing labor.
Total Direct Labor Variance
Doctors, for example, have a time allotment for a physical exam and base their fee on the expected time. Insurance companies pay doctors according to a set schedule, so they set the labor standard. If the exam takes longer than expected, the doctor is not compensated for that extra time.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Capital Account Activity in Pass-through Entities
This indicates that the company spent more on labor than anticipated, prompting a review of wage policies or market conditions. Like direct labor rate variance, this variance may be favorable or unfavorable. On the other hand, if workers take an amount of time that is more than the amount of time allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct labor efficiency variance. The total direct labor variance is also found by combining the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor time variance.
Conversely, favorable variances might indicate underutilization of labor resources, which could be a red flag for potential operational inefficiencies or overstaffing. Labor variance has a direct and often profound impact on a company’s financial statements, influencing both the income statement and the balance sheet. When labor costs deviate from the standards set during budgeting, these variances are reflected in the cost of goods sold (COGS) on the income statement. Unfavorable tax relief for taxpayers affected by oregon wildfires increase COGS, thereby reducing gross profit and, ultimately, net income. This can signal inefficiencies to stakeholders and may affect investor confidence. Labor variance is shaped by a multitude of factors, each contributing to the complexity of managing labor costs effectively.
- It is defined as the differencebetween the actual number of direct labor hours worked and budgeteddirect labor hours that should have been worked based on thestandards.
- While the overall variance calculations provide signals about these issues, a manager would actually need to drill down into individual cost components to truly find areas for improvement.
- The difference between the actual wage rate paid and the standard or expected wage rate, multiplied by the actual hours worked.
- If, on the other hand, less experienced workers are assigned the complex tasks that require higher level of expertise, a favorable labor rate variance may occur.
- There are two components to a labor variance, the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor time variance.
- In this case, the actual hours worked are \(0.05\) per box, the standard hours are \(0.10\) per box, and the standard rate per hour is \(\$8.00\).
DLYV can be affected by several factors, such as labor rate or wage changes, variations in employee skill levels, differences in the number of hours worked, and changes in working conditions. Figure 10.7 contains some possible explanations for the laborrate variance (left panel) and labor efficiency variance (rightpanel). In closing this discussion of standards and variances, be mindful that care should be taken in examining variances.
By accurately forecasting labor needs based on historical data and market trends, companies can better align their staffing levels with production demands. This reduces the likelihood of overstaffing or understaffing, both of which can lead to unfavorable labor variances. Utilizing software tools like SAP SuccessFactors or Oracle HCM Cloud can enhance the precision of workforce planning, ensuring that labor resources are optimally allocated.
Highly skilled employees tend to perform tasks more efficiently and with fewer errors, leading to favorable labor variances. Conversely, a less experienced workforce may require more time and supervision, resulting in unfavorable variances. Investing in continuous training and development can help mitigate these discrepancies by enhancing employee competencies. Another significant component is labor efficiency variance, which measures the difference between the expected hours of labor required to produce a certain level of output and the actual hours worked.
